Here we will start a self-help guide for insomnia. the guide will include the following:
- Introduction
- Symptoms of sleep problems
- Understanding sleep
- Causes of sleep problems
- what keeps sleep problems on
- Activity 1 : understand the problem
- Improve your sleep
- Get a good night’s sleep
- Waking up/nightmares
- Calm your mind
- Activity 2 : Challenge negative thoughts
- Calm your body
- Look after yourself
These points will be discussed in series over time. You can go through them first by first and when completed you can keep going thru them at your own pace or in one time.
1.Introduction
Sleep problems are common. This guide is expected to teach you the following:
- Know what are the symptoms of insomnia
- understand the sleep problems , their causes them, and perpetuating factors
- How to manage sleep problems
Sleep problems are many. You might have heard of insomnia, hypersomnia, sleep apnoea, or narcolepsy.
Insomnia is the name given to the condition when you have difficulties falling or maintaining asleep.
This guide is for anyone with sleep problems, no matter how severe is his condition. But it is not an alternative for your doctor.
2. Symptoms of sleep problems
The common sleep symptoms are as follows:
Do you have a sleep problem?
Do you think your sleep is not enough?
Do you have difficulties falling asleep or maintaining asleep?
Do you frequently feel tired during the day?
If you suffer from a sleep problem, you might recognize the following symptoms:
Your body might feel:
- tired and exhausted
- restless a lot of the time
- feeling lack of energy
- you feel heavy to get out of the bed
Your thoughts may be:
- “I will never get enough sleep.”
- “My day tomorrow will be terrible.”
- “I will remain awake the whole night.”
- “I will be sleepy at work and get embarrassed.”
Your feelings might be:
- Depressed / upset
- Anxious or tense
- Irritable
- Angry
- Worried
You might do things like:
- try to compensate sleep during the day
- use phone in bed to pass time or watch TV
- lie in bed awake during night
- keep checking the time a lot during the night
- smoke to get relaxed
- drink alcohol or use sedative pills
Your life will be affected:
- your sleep pattern may be irregular without a routine
- difficulty concentrating
- lack of motivation
- isolating yourself from family and friends
If you recognize these symptoms you probably have a sleep problem
3. Understanding sleep
Sleep is vital for life. When we go into sleep, our bodies heal and grow, organs homeostasis restored, and our brains consolidate memories.
Sleep consists of different cycles and stages, every stage is important in a distinct way.
- Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) 1 – this is a light sleep stage. In this stage you may jerk, and twitch your muscles.
- NREM 2 – in this stage your body is prepared to go into deep sleep.
- NREM 3 and 4 – deeper sleep. In this stage, your body and brain gets the most. Without it, you will not feel refreshed and energetic.
- REM (Rapid Eye Movement) – In this stage the eyelids flutter because the eyes move rapidly from side to side. Dreams that occur during this stage are recollected, and mental and emotional health and development needs this stage.
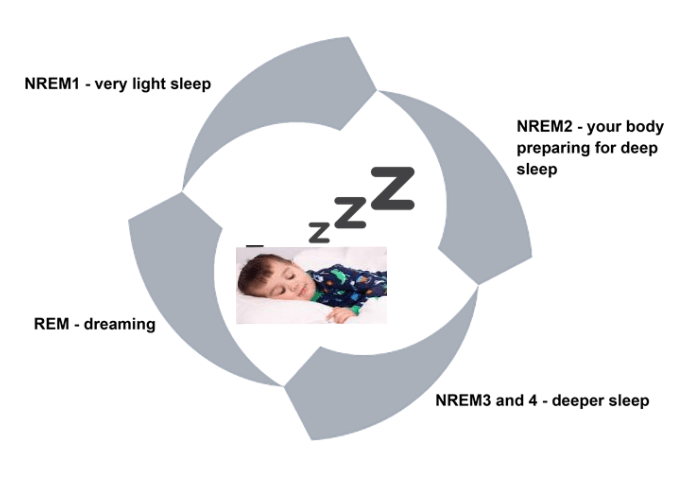
To go thru one sleep cycle of all stages it takes about 90 minutes. For a good sleep during the night you need to have 4-5 cycles.
But different people need different amounts of sleep. It depends on age, genetics and activity. If you have got enough sleep you mostly feel refreshed, energetic during the day, not sleepy, and well focused.
If during the day you aren’t feeling good, and you’re drowsy, your sleep may not be enough. You need to learn about the problem and start getting more sleep.
Types of sleep problems
Sleep problems are very common, and they can be chronic sometimes.
The most common causes are:
- Difficulty falling asleep – inability to fall asleep and lying awake on the bed for long time
- Difficulty maintaining sleep – waking up during the night or in the early morning with inability to return to sleep easily
- Bad sleep – you sleep, but on waking up, or during the day, you don’t feel refreshed or rested
4.Causes of sleep problems
There are a lot of reasons for sleep problems. Following are some examples:
Changes of life
Any big change in life can cause a sleep problem; these include things like moving to a new house, getting a new job, or having a baby. These changes can also consume a lot of your thinking and can give you different types of emotions positive or negative like excitement or worry. All these can contribute to sleep difficulties.
When the life changes are negative, like a breakup or a bereavement, your mental health is affected too. The effects can involve your sleep as well.
Mental health issues
Sleep is affected by a number of mental health conditions. Some examples are:
- depression, which can cause either a decrease in sleep or an increase with affected quality of sleep and early waking up.
- anxiety, which can make it difficult for your brain to ‘switch off’ and relax, causing difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep.
- conditions like PTSD.
- post-trauma nightmares.
Mental health and sleep are interrelated; any mental health condition is possible to affect your sleep, and any sleep problem can contribute to a mental health effect. If you think you have a mental health difficulty, consult your doctor or mental health provider.
Physical health issues
Sleep can also be affected by physical problems. Some examples are:
- any pain – chronic pain, or temporary pain from an injury or illness, can prevent you from sleep.
- bladder or bowel problems that need you to wake up for toilet during night. These include overactive bladder, bladder inflammatory conditions, irritable bowel syndrome , or inflammatory bowel disease .
- conditions that make it painful or hard to move during sleep, like arthritis, can lead to disturbed sleep.
- conditions affecting your ability to oxygenate or perfuse your body like lung diseases or heart conditions.
Drugs and other concerns
Some drugs can make it difficult to sleep, while others can cause you to sleep much or to have nightmares or vivid dreams). Other medications, like pain killers or anti-depressants, can make you feel unfocused in the morning, and cause you drowsiness.
5. What keeps sleep problems going?
Certain thoughts,feelings and behaviors can keep sleep problems going on for long periods. Though it is not your fault mostly, yet you might create habits that end up affecting your sleep. These can include:
Predicting that you will not be able to sleep before going to bed – this can lead to a ‘self-fulfilling prophecy’ where you behave as thought your prediction is right, like checking your phone. If you expect to sleep well, you’re more probably to go to bed and settle in, ready for sleep, so you fall asleep easier.
Trying to sleep when you don’t feel sleepy. Your body might not be ready to sleep at that time, although it may look as a good idea to catch up with sleep.
Doing different things on Bed.If you go to bed and spend a lot of time doing things other than sleeping, your brain can start linking being in bed with being awake. This makes it harder for your body and mind to fall asleep when you go bed.
Doing stimulating activities in bed : doing things that stimulate your mind or body (e.g.: working, watching TV, drinking tea or coffee) and similar activities will also cause your brain to link being in bed with being awake.
Repeatedly checking the time to see how long you’ve been awake – this will increase your anxiety and level of arousal and make it harder to fall asleep.
Worrying about next day: worrying about tiredness the next day, being late for work /school, or other possible worries. This worry will increase anxiety and make it hard to sleep.
Thinking about work or life – even if the topic is positive, thinking and making plans stimulates your mind and can keep you awake.
Taking naps – taking naps can make it harder for you to sleep at night.
6. Activity 1 – understanding your sleep problems
Review the previous section,and think about what could be affecting your sleep from actions and thoughts.
Answer the below questions and try to get an idea of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors can affect sleep.
Describe the situation—————————————————————————————————–
Write your thoughts
—————————————————————————————————–
Write your feelings—————————————————————————————————-
How your body felt—————————————————————————————————–
What you did—————————————————————————————————–
Try to notice how your actions, feelings and thoughts contribute to your difficulties with sleep.
7. Improve your sleep
A lot of choices are there to improve sleep and they are easy to put in operation.
Establishing a sleep/wake routine
Establishing a working day-routine is one of the most important steps towards improving your sleep.
In the morning
Create and stick to a ‘start the day well’ routine. This routine should including regular waking-up time every day. This way your body will know that it’s time to get up.
Start-the-day-well routine consists of:
- a meditation or a stretching
- brushing teeth and taking a shower
- getting dressed
- breakfast
- to-do-list of the day
- exposure to sunlight and going outside
- walking the dog or listening to some music
If it is difficult for you to get up in the morning, set your alarm. It may be better to put the alarm in the other side of the room so you will have to get up to put it off. You may spend sometime in bed before you get up fully.
In the afternoon
A good afternoon routine can result in a relaxing evening and a good night’s sleep.
This routine could consist of:
- eating lunch (follow your doctor’s advice for medications if any, weight control etc.)
- some work out like a walk, yoga , or gym
In the evening
Establish and stick to an ‘end-the-day-well’ routine that can relax your body and mind and prime you up for sleep.
Components of this routine could be:
- taking a healthy dinner
- taking a bath and brushing teeth
- putting on your sleep-gown
- taking medications if any
- a regular bedtime – don’t go to bed only if you feel sleepy
- writing down things to remember for the next day
- listening to a podcast
- reading some book
- meditation
- relaxation exercise
- gentle stretching
Things that disrupts a good routine
Some habits can get in the way of a healthy routine and should be avoided.
The following items are to be avoided:
- avoid work or study for at least an hour and a half before bedtime routine
- avoid thinking about work or tasks of the next day
- try to avoid napping
- don’t exercise too late in the day –not within 2-3 hours of bedtime routine
- avoid too much caffeine –coffee, tea, & caffeinated drinks within 6 hours of bedtime routine
- avoid alcohol too close to bedtime – 4 hours before bedtime routine
- avoid alerting activities, like a scary film or a stressful discussion
- avoid extra light right before you go to bed – especially blue-tinted light from TVs, phones, computers, gaming consoles, or tablets
- avoid staying in bed if you can’t sleep – if you can’t fall asleep after 15 minutes, get up and do something relaxing until you begin to feel dosing off again
If you have to nap, make sure your nap is finished well before 3 pm . and only nap for 20 minutes at most. If you nap regularly,start by reducing the length of your naps gradually
8. Set Up the Night For Good Sleep
You can make sure that your routine is working by a number of steps. These are supposed to help you fall asleep, stay asleep, and wake up refreshed.
The environment
Your sleeping space should be relaxing and comfortable. Try the make the setup for that.
Bedroom
Arrange your room to be soothing, comfortable and relaxing. It is useful to get rid of the mess and clutter.
Bed
Your bed should as comfortable as possible – bedding should be clean, and washed regularly. Try a lavender scented pillow.
Light
the room should be protected from light noise. To make it dark use curtains and blinds. Sometimes, eye mask/fold could be helpful.
If you are not comfortable with the dark, use a night light to help you get relaxed.
Try not to have a TV or computer in the room. If you have one in the room, turn it off.
It is helpful to get your phone out of reach if you think you ill use it or check the time on it.
Sound
Try to keep your room as quiet as you can. If there’s noise coming into the bedroom, wearing earplugs might be helpful.
The room should be as quiet as possible. If you cannot control the noise, you may try to use earplugs then.
Sometimes it is helpful to have some background music or sound, in this case don’t use the TV for this purpose.
Temperature
The temperature should be comfortable, neither too hot nor too cold. sometimes it helps to keep the room cold and the bed warm – for example, open the window, but use a heavy blanket or duvet.
The routine
These routines are to help you get a restful night sleep but they are not everything. You can always change the routines. The important thing is to get your body and mind adjusted to better sleeping habits.
It is not necessary to have everything perfect. sleep is a natural thing and the default is to have it. If you don’t have it then there is some obstacle. You don’t have to exert the efforts to get sleep but to identify the obstacle and leave the sleep wake cycle take its natural path.
If you found how to get your mind and body adjust to better sleep habits, you may not even need the routines.
9. Waking up/nightmares
Sometimes the problem is not falling asleep but staying asleep. It could be that you wake up during the night and cannot go back to sleep or it could be a nightmare.Try these tips to go back to sleep.
How to sleep again.
- Remind yourself that it is normal to wake up during the night. This decreases your worry and reduce your hyper-arousal and can help with frustration, and anxiety.
- Learn a relaxation or meditation exercise and try it to bring you back to sleep. One meditation exercise is below
- If you remained awake after about 20-30 minutes, get up, go out of the room and try doing something peaceful, like reading a book, or listening to quiet music.
- Avoid TV and arousing activities. Stay until you feel sleepy again and go back to bed.
Body Scan meditation for sleep from UCLA:
Repeat theses steps as needed during the night. This way your brain will learn that bed is for sleep and not for waking up.
Waking up in the middle of the night is sometimes a symptom of some health issue, so it could be good to consult your doctor to rule out any health problem.
What if it is a nightmare
- Remember that you are at home safe and sound. Name the objects around you in the room , house or around the house . You may look out the window to get connection with the real world.
- Try to think of a good ending to your dream. Manipulating dream is one good option to thwart a nightmare.
Make your back-to-reality kit at hand:
- put a wet towel or a water spray at your side to refresh your face as soon as you wake up.
- have a soothing object beside you, as a soft toy or a photo.
- sniff some perfume you like on waking up from a nightmare.
These can help you go back to reality.
If your nightmare is due to incident in your life, it is better to consult your counselor or physician.
10. Calming down an aroused mind
If you happen to lie awake at night and worry, this can make it hard for you to fall asleep and remain asleep. Setting aside ‘worry time’ is one way to fix this – ‘worry time’ is a period during the day you allocate it to focus on your worries. This can help decrease the time you spend thinking about them at night.
Worry time:
- Determine a time in the day and call it worry time – it should be about 10 to 15 minutes.
- Have a notepad handy at your bedside table and write down any worries that arise at night. Remind yourself that you have worry time for them during the day.
- When your worry time arrives during the day, let yourself worry about the things you’ve written in your notepad. Note down possible solutions or plans while you’re focused on your worries.
- Stop as soon as your worry time is finished – or earlier, if you run out of worries before the 15 minutes is up. After the 15 minutes are up, start writing down any worries for your next worry time.
Relaxation
If you are one of the people who have a busy mind most of the time, then try some relaxation exercise to help you drop off to sleep or go back to sleep after you wake up. You may check the meditation audio in our previous series of this guide or try the following breathing exercise. This exercise involves focusing on and slowing down your breathing.
- Get into a comfortable position in bed.
- Try to breathe in a steady rhythm. It can help to visualize imaginatively something steady and repetitive, like waves coming in and going out, or a balloon inflating and deflating.
- You could also count: for example, “in, 1,2,3… out, 1,2,3”.
- Repeat the steady breathing for a few minutes.
It’s natural for your mind to wander and distract you when doing this exercise. Continue practicing and don’t get discouraged. It takes time to get used to relaxing and focusing like this, and getting distracted doesn’t mean you’re doing anything wrongly.
11. Activity 2 – Challenging thought mistakes
This activity is designed to teach you how to argue with yourself on the negative thoughts about sleep, check them logically and discard the error thinking. The goal is to replace the unhelpful thoughts with calming ones. Try to use the thoughts you wrote down in the first activity as a starting point.
It will benefit you too to record how much your worries reduce as a means to check progress.
Complete the following table to challenge your Negative thoughts
| The Question | Your Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the situation | ……………………………………………………………………. |
| What are you feelings/emotions | |
| Negative thought behind your feelings | |
| Evidence for and against the negative thought | |
| Is there an alternative way to think of the situation? | |
| Rate how much you believe in the new thought from 0% to 100%. | |
| Rate how strong your feelings are now, from 0% to 100% |
12. Relaxing your body
Tense and restless body will prevent sleep and cause you to toss and turn in the bed. Some relaxation exercise can help you relax your body,calm mind and facilitate sleep.
Try to do this exercise:
Progressive muscle relaxation
This is better done lying on your back in a comfortable position. If you need some pillows to support your knees just do it.
This exercise involves the whole body but if you have some tender or main part of your body just miss that part.
Go through each part of your body – you mat follow this order:
- Right hand and arm
- Left hand and arm
- Right leg and foot
- Left leg and foot
- Stomach
- Chest
- Back muscles
- Shoulders
- Neck and throat
- Face
Do as follows:
- Tense up your right hand and arm and hold it for a few seconds as you breathe in.
- Release the tension as you breathe out.
- Do this for each body part.
- Next, lightly tense up your right hand and arm as you breathe in, with just enough tension to notice.
- Release the tension as you breathe out.
- Do this for each body part.
- Finally, focus on each body part in turn and concentrate on just releasing it while you breathe normally. This can help you release any final tension in your body.
You may listen to this audio from Alberta website:
13. Looking after yourself
Lifestyle can affect the sleep dramatically and some styles are very unhealthy for sleep, body and mind.
Overcoming these habits is not easy and becomes very hard with time. But making some efforts to replace the negative habits in your lifestyle with healthier positive ones can improve your sleep enormously.
Below is a list of tips that will help you get started :
Alcohol
Many people resort to alcohol to help them sleep. However, alcohol affects sleep negatively and decreases the quality of sleep. Drinking in fact disrupts normal sleep-wake cycle. It also puts more stress on your body system because the body needs to process and excrete it.
On average the body needs one hour to metabolize one unit of alcohol. This is affected by a number of factors such as how old you are and how heavy. So if you cannot abstain try to stick to the recommended guidelines for alcohol consumption and keep some time between your last drink and the bedtime.
If you’re regularly drinking more than the recommended guidelines, or you’re concerned about your alcohol use, there is help available. Many people find themselves drinking alcohol to try to cope with low mood, anxiety, or other mental health issues. Our resources on alcohol offer more information and help.
If you’re regularly drinking more than what is in the guidelines, it is time to take some action. People feel that alcohol helps them managing anxiety, depression, social anxiety and some other mental issues, but this is not true and it backfires at the end. If you have concerns on your drinking consult your doctor and seek help to abstain.
Nicotine
Nicotine and similar substances are neurological stimulants. They may cause you fell calm at first but later they can keep you alert and make it harder for you to fall asleep.
The myriad harmful effects of smoking make it always warranted to quit
Substance use/Qat
In a survey conducted by Staff Counseling unit in sana’a in 2018 , the percentage of local staff using qat regularly is 56% with 95% credible interval between 48% and 64%.
Comparing males to females, it was found that males are more probable to use qat than females. Percentage of male staff using qat is 73%, and only 27% of females.
The chance that a staff member chews qat if he is female is only 19% , whereas the chance that he is chewing qat if he is male is 81%.
Other substances are used by people to help them cope, for recreation,and to manage difficult feelings. Some people self-medicate with prescription drugs unnecessarily.
Some substances are stimulants and disturb normal sleep. Others are sedative but they lose effectiveness overtime.
If you using such substances, it is better to start seeking help and getting rid of it.
Healthy Diet
A healthy balanced diet is very useful to regulate sleep.
It is better to take dinner at least 2 hours before bedtime.
Use regular meal times with plenty of water.
Physical Activity
Keeping fit and active is good for both physical and mental health. Regular exercise can help you fall asleep faster, and wake up less during the night.
Regular physical activity and exercise are essential for mental and physical health. They help you fall asleep faster and less awakenings during night.
make sure that you don’t exercise within 2 hours before bedtime since it will make you aroused more.
Pingback: Insônia – Home Page